They are used to lift and pull heavy containers in Ship-To-Shore Cranes (STS), Rubber Tyre Gantry (RTG), and Straddle Carriers. I can also see them on my way to work in different construction machines, and I feel their usefulness when I use the elevator of the building where I live.
But they are not only used in handling heavy loads! They also serve as structural support cables in large static structures like The Mohammed VI Bridge, the longest cable-stayed bridge in Africa, linking the capital city of Rabat to the city of Salé.
Getting optimum life out of dynamic steel wire rope is one of the key strategies within a maintenance program. A simple discussion with maintenance folks in the field will reveal that wire ropes are a big issue. In this article, I will not dwell on dimensional characteristics but focus on the lubrication side of dynamic steel wire ropes.
I will explore how to keep dynamic steel wire ropes youthful through relubrication, starting by shedding light on the importance of relubricating dynamic steel wire ropes, then reviewing the types of lubricants used. This article concludes with different possible methods to relubricate dynamic steel wire ropes and the best practices for effective dynamic steel wire rope relubrication.
Why Is Lubricating Dynamic Steel Wire Rope Required?
Adequate and proper lubrication is vital to keeping dynamic steel wire rope running at its best. DIN 15020 standard explains that lubricants in wire rope diminish friction and corrosion between the groove and the wire rope and between the individual wires.
The same standard explains that shorter rope service life should be expected if the wire rope lubrication is stopped for operational reasons. Thus, lubrication is essential in the steel wire rope life cycle.
It considerably impacts its operability and aims to support the integrity of the wire ropes with continued safe and effective operations. Lubrication could eliminate or minimize most of the causes of wire rope failures. We can segregate between 3 tiers for steel wire rope lubrication:
Lubrication Of Dynamic Steel Wire Rope During The Manufacturing Process
Individual steel wires are subjected to extensive bending, twisting, and tension during their manufacturing process to form the rope. These actions generate friction between the individual wires and strands, leading to wear and potential damage.
The lubricant helps the wires move smoothly through manufacturing machines. Also, it helps create a protective layer between the wires to allow slight movement between them and minimize the risk of wear and corrosion. ISO 4346 Standard specifies the nature, properties, and basic requirements of lubricants used to manufacture wire ropes for general purposes [2].
Lubrication Of Dynamic Steel Wire Rope During Storage
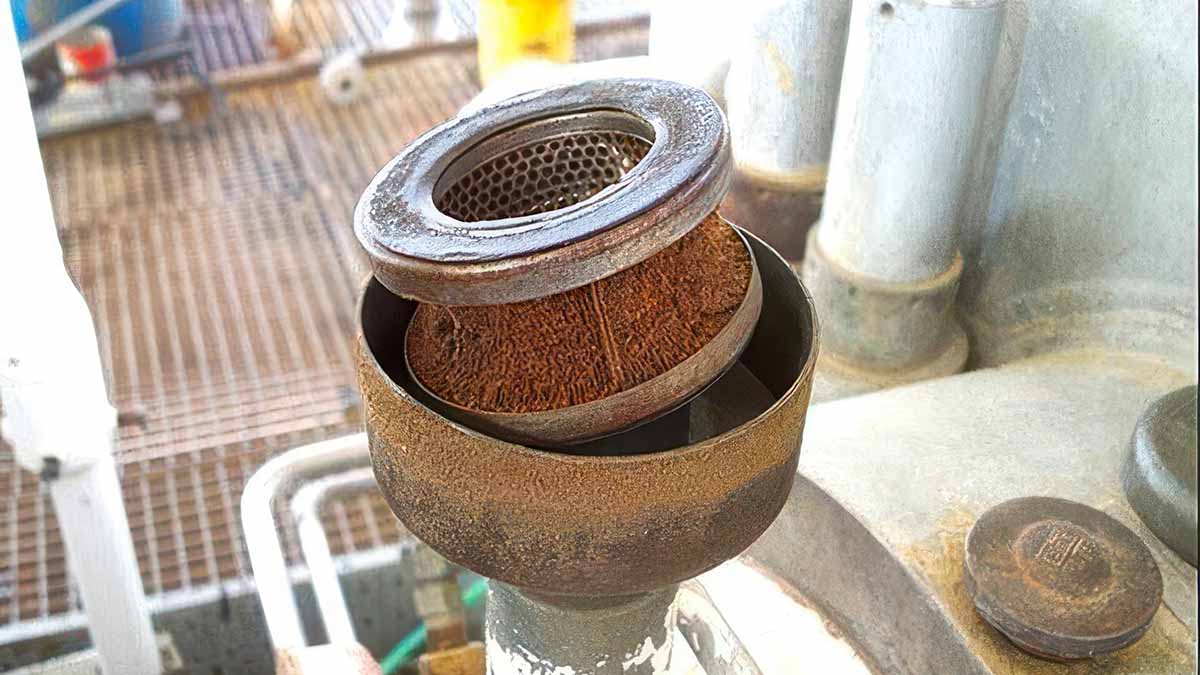
Dynamic steel wire ropes depart the manufacturing plant saturated in lubricant. During their storage, wire ropes can be exposed to several factors affecting their performance and longevity after deployment.
Direct exposure to rain or snow, humidity, temperature changes, and chemicals increases the risk of corrosion before deployment. Proper lubrication is essential in protecting their structural integrity and readiness for use.
Regular wire rope inspections during storage can help determine when relubrication is necessary. Signs of wear, corrosion, or excess dirt and debris may show the need for relubrication.
Additionally, wire ropes stored for an extended period without use may require relubrication to ensure they are still in optimal condition before installation. If necessary, apply a suitable preservative or lubricant compatible with the rope manufacturing lubricant [3].
Lubrication Of Dynamic Steel Wire Rope In Service
During operations, a steel wire rope is bent considerably. The wires and the strands move against each other. Relative movements also occur between the wires in stranded ropes changing the tensile forces by friction. There are also movements between wire ropes and sheaves [4].
On the other hand, steel wire ropes must withstand demanding working conditions (heavy loads, constant friction) and harsh environments (exposure to dirt, chemicals, moisture from rain or high humidity, and other contaminants). These factors can cause the wire rope to deteriorate over time, leading to loss of strength, wear, and eventual failure. Lubrication helps to minimize the effects of these factors by:
- Reducing internal (metal-to-metal contact between wires and strands) and external friction (wire rope exterior surfaces with grooves).
- Enhancing flexibility.
- Mitigating fatigue failure.
- Protecting from external contaminants.
- Preventing Corrosion.

A dynamic steel wire rope that is properly lubricated (Right Lubricant, Right Quantity, Right Method) will last three times as many working hours or cycles as one that is poorly lubricated. An improvement of up to 300% can be expected from a correctly lubricated rope compared with a similar unlubricated rope [5]
What Is the Right Lubricant For Dynamic Steel Wire Rope Relubrication?
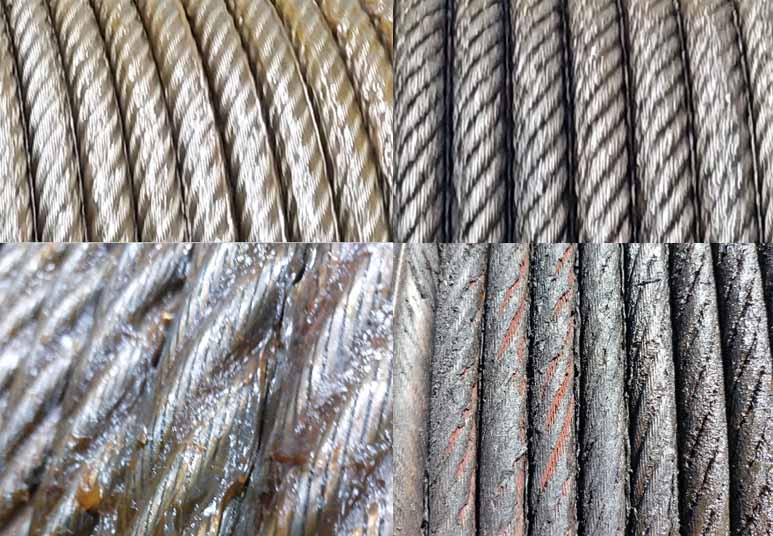
To make dynamic steel wire rope conduct its duty smoothly while being protected from external contamination and corrosion, consider two categories or types of lubricants: penetrating and surface coating lubricants.
Penetrating Lubricant
Dynamic steel wire ropes may fail from the inside with regular use. Penetrating lubricants are intended to reach the steel wires in the strands and rope core to reduce friction and wear during normal use and provide maximum protection against corrosion. Desired properties for penetrating lubricants are:
- In grease, suitable consistency, drop point, thickener, and base oil viscosity with friction modifiers additives (AW & EP).
- In the case of oil, suitable base oil viscosity with desired additives (AW & EP).
In both cases, the lubricant should withstand the elevated temperatures generated during wire rope operation and have excellent water and oxidation resistance.
Coating Lubricant
The coating lubricant should act as a barrier and seal to protect the outside of the wire rope from moisture and contaminants. Desired properties of coating lubricant are:
- Corrosion prevention
- Resistance to hot temperatures and water/wash
- Sufficient adhesive strength to allow the lubricant to remain on the rope
It is advisable to avoid asphaltic compounds because they dry into a dark hardened surface that makes inspection and cleaning difficult.
Several lubricating products can be used to relubricate dynamic steel wire ropes, including greases, oils, and dry lubricants. The choice of lubricant will depend on the application, environment, and operating conditions.
When selecting a lubricant for dynamic steel wire rope, make sure it complies with the recommendation of the steel wire rope manufacturer.
What Is the Right Quantity of Lubricant To Use While Relubricating Dynamic Steel Wire Rope?
The amount of lubricant applied is critical. Over-lubrication can lead to excess buildup and attract dirt and debris, while under-lubrication will not adequately protect the wire rope and lead to increased wear. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations, applying the right lubricant amount can help ensure optimal lubrication and wire rope protection.
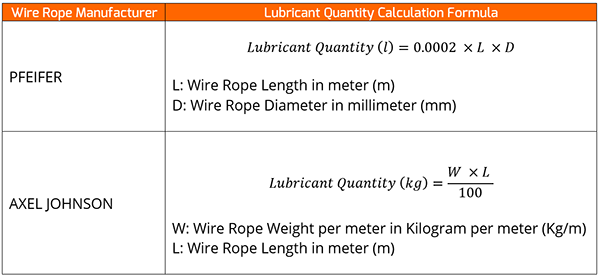
Examples of lubricant quantities calculation formulas provided by wire rope manufacturers.
Relubrication Intervals for Wire Ropes
After the wire rope is put into service, the original lubricant is lost gradually with normal use. Regular relubrication is essential to ensure the wire rope’s longevity. However, the relubrication frequency is difficult to manage as it depends on various factors, such as the application and operating conditions, including load, speed, and environment.
With wire rope relubrication, we should differentiate between coating lubrication and penetrating lubrication. The coating lubrication frequency follows the inspection frequency. Before visual or magnetic inspection, the wire rope should be cleaned (remove the coating lubricant). After the wire rope inspection, the coating lubricant should be re-applied.
However, as a rule, dynamic steel wire rope relubrication intervals should be scheduled per the wire rope manufacturer’s recommendations and the equipment manufacturer where it is installed. Without such instructions, lubricate wire ropes for benign operating conditions at least once a year.
More frequent lubrication would be necessary for severe operating conditions and environments to maintain optimal performance and prevent wear and corrosion.
Methods to Relubricate a Wire Rope
Relubricating wire ropes should be preceded all the time by cleaning. Any residual coating lubricant and contaminants should be removed first before applying any new lubricant. There are three common methods for wire ropes lubrication: [6]
Manual Lubrication
Manual lubrication involves applying the lubricant to the wire rope by painting, Swabbing, or brushing. It is typically used only for coating outer wires and is suitable for wire ropes not exposed to elevated temperatures. When using oil, a spray can be used for the wire rope relubrication.
Manual Lubrication (painting) of wire ropes is time-consuming and poses safety and environmental issues. Technicians come into close contact with lubricants and may have some safety concerns due to broken strands and intensive labor.
Additionally, manual lubrication will use more lubricant than other methods, probably resulting in poor lubricant penetration. The more lubricant quantity used, the greater the lubricant cost and risk of environmental impact.
Semi-Automatic Technique
The drip, spray, or trough method can apply the lubricant. These methods apply the lubricant at a single point and use the rope’s movement to spread the lubricant over the entire length of the system.
Automatic Technique
Pressurized lubricant application is the best relubrication method for wire ropes. This approach utilizes a pump, the force of the pressurized lubricant between the wires and into the wire rope’s small vacant spaces.
This mode provides maximum penetration of the lubricant into the gaps of the wire rope, enables the lubricant to adhere to each wire, and offers the best protection against corrosion. Side benefits from the pressurized application include less safety risk to technicians and less chance of environmental impact from routine care.
Best Practices for Wire Rope Lubrication
To ensure adequate dynamic steel wire rope lubrication, follow these best practices:
Do’s
Lubricant Compliance
Use the right lubricant suitable for the wire rope material and application. Consider the factors mentioned above and follow recommendations from the wire rope manufacturer to ensure compatibility and effectiveness.
Cleaning Before Relubrication
Before applying the lubricant, clean the wire rope thoroughly to remove any dirt, debris, or any other contaminant from the outer strands and in the valleys of the wire rope. A wire rope cleaner could be used. This will enable a proper penetration of the new lubricant and enhance the corrosion protection to optimize wire rope lifespan.
In case of dirty wire rope, hardened lubricant, or accumulated layers of the old lubricant or other contaminants, the wire rope should be cleaned with a wire brush and petroleum solvent, compressed air, or steam cleaner before relubrication. For this, use only compatible cleaning fluids, which will not impair the original rope lubricant nor affect the rope-associated equipment.
Lubrication Method
Use the wire rope lubrication proper method, which will facilitate the application of the lubricant evenly over the wire rope full length.
If the lubricant contains a diluent that evaporates after exposure to the atmosphere, the lubricant should be given 4 to 8 hours to ‘cure’ before the device is returned to service.
Safety
All mandatory Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) shall be worn in addition to the relevant PPE if needed. If cleaning by brush, eye protectors must be worn. If using fluids, understand that some products are highly inflammable. Wear a respirator if cleaning with a pressurized spray system.
Don’ts
Lubrication Method
Over-lubrication can cause the lubricant to accumulate and attract dirt and debris, leading to wire rope wear.
Safety
Don’t discount the potential safety hazards of working on a moving rope.
Please don’t attempt to clean and lubricate the wire rope while it is suspending a load unless otherwise stated in the OEM’s instruction manual or other relevant documents.
Proper lubrication is essential for protecting the dynamic steel wire rope against corrosion and contaminants and for protection from wear and other potential damage. Select the right lubricants, following the most suitable application method, and lubricate at the optimum frequency.
A helpful starting point would be a review of the lubrication recommendations and any specific requirements specified by the wire rope manufacturer and OEM of the equipment.
Precision lubrication is vital for extending wire rope lifespan but is not the only parameter to address. Proper storage conditions, handling, precision installation, and regular inspection can help prolong the service life of the wire rope and reduce maintenance costs.
[1] DIN 15020: Lifting Appliances; Principles Relating to Rope Drives; Calculation and Construction.
[2] ISO 4346: Steel wire ropes for general purposes — Lubricants — Basic requirements.
[3] ISO 4309: Cranes — Wire ropes — Care and maintenance, inspection, and discard.
[4] Wire Ropes; Tension, Endurance, Reliability; Second Edition; Klaus Feyrer. pp 31 to 33.
[5] Lubrication and Reliability Handbook; M.J. NEALE pp A10.1 from to A10.3.
[6] Handbook of Lubrication and Tribology; Volume I: Application & Maintenance; Second Edition; George E. Totten. pp from 15-1 to 15-6.