Calculating the beta rating for an oil filter involves understanding how effective the filter is at removing particles of a certain size from a fluid. The beta rating is a standard measure used in filtration to quantify the filter’s efficiency, specifically its ability to capture particles of a given size. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the beta rating is calculated:
Understanding the Beta Ratio
The beta ratio (β) is defined as the ratio of the number of particles of a specific size (or larger) entering the filter to the number of those particles exiting the filter.

Beta Ratio Key Concepts
- Upstream Particles: These are particles in the fluid before entering the filter.
- Downstream Particles: These are particles present in the fluid after it has passed through the filter.
Beta Ratio Calculation
Step 1: Measure Particle Count Upstream: Count the number of particles of size x microns or larger in the fluid before it enters the filter. Let’s call this number Nu
Step 2: Measure Particle Count Downstream: Count the number of particles of size x microns or larger in the fluid after it has passed through the filter. Let’s call this number Nd
Step 3: Calculate the Beta Ratio: Use the formula to calculate the beta ratio:
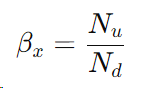
Step 4: Determine Filtration Efficiency: The filtration efficiency can be determined from the beta ratio using the following formula:
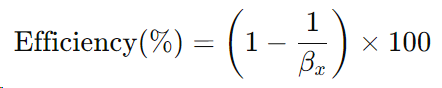
For example, if , the filtration efficiency is:
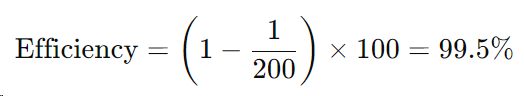
Example Beta Ratio Calculation
Let’s say you have an oil filter, and you want to determine its beta rating for 10-micron particles:
Upstream Particle Count ( ): 200,000 particles of size 10 microns or larger.
Downstream Particle Count ( ) 1,000 particles of size 10 microns or larger.
Beta Ratio Calculation:
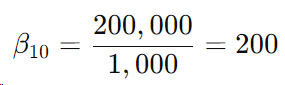
Filter Efficiency Calculation:
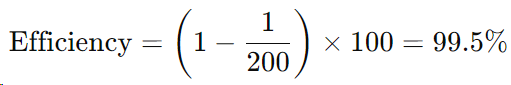
Interpreting the Beta Rating
- A beta rating of 200 means that for every 200 particles of 10 microns or larger entering the filter, only 1 particle exits. This results in a 99.5% efficiency for capturing 10-micron particles.
- Higher beta ratios indicate better filtration performance. For instance, a beta ratio of 1000 would mean an efficiency of 99.9%.
Variables Affecting the Beta Ratio
- Filter Media: The type of filter media significantly impacts the beta rating, as some materials are more effective at capturing smaller particles.
- Flow Rate and Pressure: Flow rate and pressure changes can vary the filter’s performance (and thus the beta rating).
An oil filter’s beta ratio is a straightforward yet powerful metric for assessing its efficiency in removing particles of a specific size from oil. It gives maintenance and reliability professionals a precise measure of the filter’s performance, which is critical to maintaining mechanical system health.